The bank transfer process between domestic and international spaces requires an understanding of SWIFT codes and routing numbers. These payment-routing systems exist for different functions because they operate in separate financial systems. The international banking communication system SWIFT codes support secure cross-border transfers, but routing numbers enable domestic fund transfers in the United States.
We will break down how these codes operate, their similarities and differences, and where to access them.
Key takeaways
- The purpose of SWIFT codes is to make international transfers, while the main role of routing numbers is to facilitate domestic ones.
- SWIFT codes use a numbering system that includes 8-11 alphanumeric characters, but routing numbers are limited to 9 digits only.
- SWIFT grants its codes to organizations through its Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication platform, while the American Bankers Association distributes the routing number system to financial institutions.
- SWIFT codes recognize international financial entities and routing numbers are used by banks and credit unions within the US.
What are SWIFT Codes?
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications) is a financial network that allows communications to be secure between banks around the world. A SWIFT/BIC code uniquely identifies a bank or financial institution globally, including its country, location, and branch (if applicable), facilitating international transactions.
If you want to send money from the United States to an international destination via wire transfer, you will need to know your recipient’s SWIFT code. SWIFT is the most widely used system for international money transfers.
What is the Format of a SWIFT code?
The SWIFT code contains 8 to 11 characters, which are further divided into four categories.
- The first four characters: A code representing the bank, often a shortened form of its name.
- The following two characters: Show the country where the bank is located.
- The next two characters: Indicate where the bank’s main office is.
- The last three characters (optional): Identify the specific branch of the bank. If “XXX” is used, it means the bank’s main office.
For example, if the SWIFT code is EXMPUS33ABC.
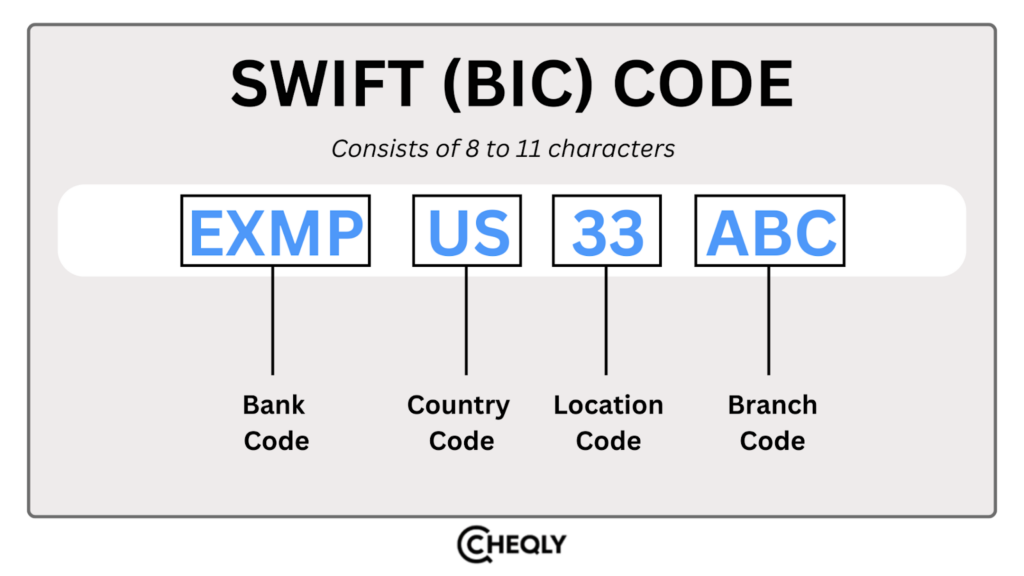
- EXMP: A code that represents the bank.
- US: The country where the bank is located (United States).
- 33: Shows the location of the bank’s main office.
- ABC: Identifies a specific branch of the bank (if applicable).
What are Routing Numbers?
The United States’ banks and credit unions use a routing number, which is a nine-digit code that makes domestic transfers more efficient and also identifies the financial institution involved in the transaction. It can be used for a number of transactions, such as ACH transfers, direct deposits, and check processing.
Since the American Bankers Association started giving each financial institution a distinct nine-digit identifier in 1910, routing numbers have existed. They are also known as the routing transit number (RTN) or the ABA (American Bankers Association) routing number.
What is the Format of a Routing Number?
Routing numbers are 9-digit codes that identify the bank where the account was opened.
- The first four digits normally indicate the Federal Reserve district and the bank’s branch.
- The next four digits identify the bank or financial institution.
- The last digit is a check digit for validation.
For example, if the routing number is 123456789.
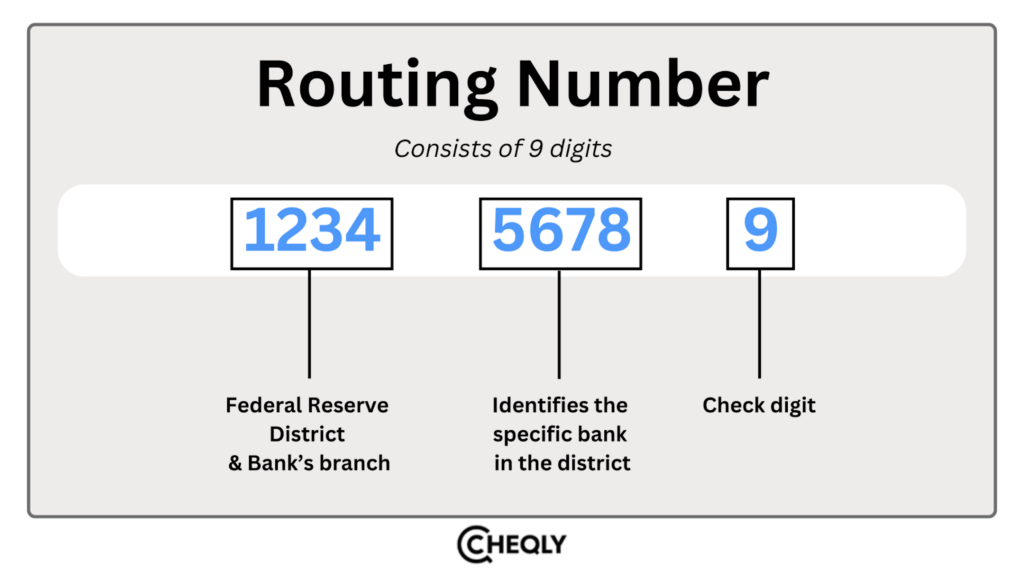
- 1234: It shows the Federal Reserve district and the bank’s branch.
- 5678: This identifies the specific bank (in this case, a bank in that district).
- 9: The check digit that verifies the number is correct.
SWIFT Codes and Routing Numbers: How Do They Work?
Routing numbers and SWIFT codes make it easier to process payments. This part offers a detailed understanding of how each system works.
SWIFT Codes
Payment instructions can be sent and received between banks and financial organizations worldwide because of the SWIFT network. In 200+ countries, almost 11,000 banks and other financial institutions use the network. Banks, clearing houses, brokerages, and asset management firms are included. The codes inform the SWIFT system of the transfer’s origin, destination, and delivery method.
Both the sender and the receiver should use the specialized SWIFT codes of their banks to send a payment to a bank situated in another country.
Routing Numbers
They help identify banks in the US and make it easier to process domestic transactions. These nine-digit codes make sure payments go to the right bank and also speed up things like ACH transfers, direct deposits, and check processing. Each bank gets its own unique routing number to avoid confusion with others that have similar names. Since routing numbers are only used for payments within the US, they help ensure that your money is sent and received safely.
Both savings and checking accounts require banks to use routing numbers. This number is needed for autopay setups or transferring funds but not for debit or credit card purchases.
Differences Between SWIFT Codes and Routing Numbers
Here’s a quick comparison of SWIFT codes and routing numbers:
| Feature | SWIFT Code | Routing Number |
| Purpose | International transactions | Domestic transactions within the US |
| Format | 8 to 11 characters (letters and numbers) | 9 digits |
| Geographical Use | Used globally for cross-border payments | Used only in the U.S. for domestic payments |
| Required Info | Identifies the recipient bank for international transfers | Identifies the bank for US domestic transfers |
| Transaction Types | Wire transfers, international payments | ACH transfers, direct deposits, check payments |
| Assigned By | Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) | American Bankers Association (ABA) |
Where can SWIFT Codes and Routing Numbers be Used?
If you are sending money abroad, it is essential to have the recipient’s SWIFT code. (Some countries don’t have SWIFT codes, so you will need to find another way to identify your bank for electronic transfers or use a different method to transfer the money.) Similarly, receiving money from abroad requires you to provide your SWIFT code to the sender.
To send money within the US, you need the other person’s bank routing number. You also need to give your routing number for transfers, direct deposits, and online payments.
Where You Can Find Your SWIFT Code or Routing Number
Here’s how to quickly find your SWIFT code or routing number.
SWIFT Code
- You can check it on your account statements or online.
- Check your bank’s website.
- You can also call your bank for help.
Routing Number
- Check the bottom left corner of your checks. The first nine digits (starting with 0, 1, 2, or 3) are the routing number. Next is your account number, followed by the check number.
- Log into your account and look for “Account Info” or “Account Summary.”
- You can also find it by searching online with your bank’s name and “routing number.”
Simply put, a good knowledge of the difference between SWIFT codes and routing numbers will help you send your money more effectively and securely. SWIFT codes are used in international transfers, whereas routing numbers handle transactions in the U.S.
The SWIFT code or ABA routing number you need to use will depend on the transaction type and the bank location. If you’re not sure which code to use for a particular transaction, it’s always best to ask your bank for advice.
SWIFT Code vs. Routing Number FAQs
The following are some common questions and answers related to SWIFT codes and routing numbers:
Is a SWIFT code required for domestic US payments?
No, SWIFT codes are exclusive for international transfers and are not used to make domestic money transfers within the US.
What happens if the SWIFT code provided is incorrect?
Incorrect SWIFT Code could delay or direct cross-border fund transfer to the wrong place. Make sure you always double-check the code before sending money.
Can I use just a routing number for an international wire transfer?
No, international transfers use a SWIFT code. A routing number serves only for internal transactions inside the United States.
What happens if I use the wrong Routing Number?
An incorrect routing number may end in failed transactions, delays, or even letting the money go to the wrong account. Double-check the routing number prior to the transfer of funds.
How long does a transfer take using a SWIFT code vs. a routing number?
Typically, SWIFT transactions on the basis of the bank and intermediaries take 1 to 5 working days, while domestic transfers through routing numbers are usually faster, as they are completed within 1 to 2 days.
Make your international transfers easier with Cheqly!
Cheqly makes it easy for small business owners to manage international wire transfers. It sends and receives payments across borders quickly, securely, and smoothly. It also gives users clear instructions, tracks payments in real time, and provides reliable customer support to ensure seamless transactions.
Open a Cheqly business account and make your international transfers easier.
