Payment rails refer to the core infrastructure that makes it possible to transfer funds electronically between parties in a financial transaction. Like train tracks directing a train, payment rails offer a secure, defined route for money to flow seamlessly from payer to payee across different banks and platforms.
These networks let users make all kinds of transactions, from moving money between local accounts to sending funds across the world quickly and accurately. Choosing the right payment rail is important to get the best speed, cost, security, and fit for your business, since each rail works differently in terms of settlement time, fees, and use.
This article will guide readers through key payment rail types—including ACH, wire transfer, card networks, and real-time payment rails—comparing how they operate, their pros and cons, and helping businesses select the most suitable payment solution for their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Payment rails are financial systems that transfer money between payers and payees electronically.
- Major types include ACH, wire transfers, card networks, real-time payment systems, SWIFT, and paper checks.
- Each rail differs in settlement speed, cost, security, and geographic capability.
- The ideal rail depends on transaction speed, cost, coverage, business size, and use case.
- Choosing the right rail can result in lower fees, improved cash flow, and smoother payments for domestic and international business.
What are payment rails?
A payment rail is used whenever a non-cash payment is sent or received.
The payment infrastructures that enable money transfers between the payer and the payee are referred to as payment rails. The word “rail” conjures up the idea of train tracks, which serve as the digital infrastructure linking different financial institutions and enterprises.
These payment systems provide a clear path for moving funds from point A to point B and can be used for both domestic and international payments.
What kinds of payment rails are available?
There are now about six different payment rails in the US. However, as the banking industry develops new and better methods of sending money, this number is always changing.
Among the most widely used payment methods are:
- Payments made through the Automated Clearing House (ACH)
- Rails for cards
Although the phrase is most frequently used to refer to non-cash and digital forms of payment, technically, even currency would be regarded as a type of payment rail. However, each payment rail is unique. Every rail has advantages and disadvantages, and works best in particular circumstances.
How do payment rails work?
Payment rails function by sending data between financial companies since they are designed to enable digital transactions. This information includes facts like:
- Details about the customer’s account
- MIDs, or merchant identification numbers
- Directions for the financial organization
- Details about the transaction
Keep in mind that the payer and the payee’s bank accounts must be connected to the same network in order for the payment train to function. The transaction may incur additional fees based on the payment rail you choose. Settlement timeframes can also vary.
What’s the cost involved in using a payment rail?
You will have to pay a fee of some kind when you make a non-cash payment. Although the precise amount varies from rail to rail, each transaction will often have a minor sum added to it.
Whereas wire transfers may have higher costs, ACH transactions are typically the most economical. Similarly, domestic payments are usually less expensive than international ones.
Again, the specific expenses and charge structures might change, so business owners should be mindful to consider these expenditures in their financial operations.
What is settlement time?
You must factor in “settlement time,” or the interval between the start of the transaction and the arrival of the funds in the recipient’s bank account, while processing digital payments.
Different rails have varying settlement times. A short period is preferred by most organizations, as it allows them to better access their operating cash flow.
Only recently has the Real-Time Payment (RTP) network enabled real-time payments; other rails provide a settlement time of 24 to 72 hours. To guarantee that transactions are completed within the same business day, certain banks now provide same-day ACH payments.
Types of Payment Rails
Payment rails come in different forms, each with unique features that make them suitable for certain tasks. Below is a description of the essential payment rails.
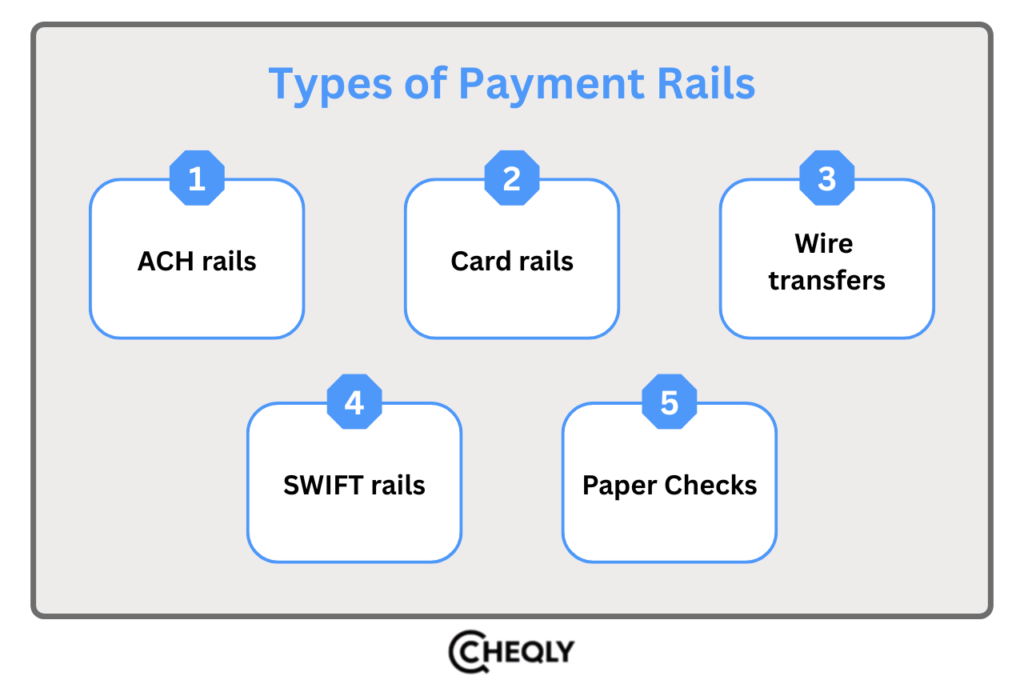
ACH rails
The ACH network allows users to move money from one bank account to another in a fast and cost-effective manner. In the US, both the sender and receiver must have bank and routing numbers, as ACH payments cannot be processed without them.
Card rails
Merchants favor card rails because they allow both offline and online transactions. Typically, customers opt for cards due to their familiarity with major card networks rather than with ACH or other digital channels.
Wire transfers
Wire transfers are very secure, as banks ensure delivery; however, they can sometimes be expensive. Transactions can be carried out at the bank or through intermediaries. They are a good option for large transactions or if no other options are available. Fees can vary, so it is always advisable to check before transferring.
SWIFT rails
International business can be conveniently facilitated through the SWIFT system, as it handles several currencies and foreign exchange operations. Nevertheless, these transactions usually take 3–5 business days and are typically more expensive than other payment methods.
Paper Checks
In spite of being old-fashioned, paper checks are still useful. Most banks nowadays provide mobile deposits, which are usually free of cashing fees. However, in the case of large transactions, many customers still rely on the security of checks rather than digital solutions.
What are the key differences among the major payment rails?
Each payment rail is different in terms of speed, cost, security, and usability. When a company knows these differences, it becomes easier for them to select the most appropriate way to meet their needs.
| Payment Rail | Speed | Cost | Geography | Use Case | Security | Settlement Time |
| ACH | Slow (1-3 days) | Low ($0.20–$1.50) | Domestic/limited intl. | Payroll, recurring | Strong | 1-3 days |
| Card Networks | Fast/Instant | Moderate (1.5–3.5%) | Global | Retail, Online | Strong | Seconds – minutes |
| Wire Transfers | Instant few hours | High ($20–$50) | Global | Large/value tx, B2B | Strong | Same-day |
| SWIFT | Slow-medium | High (varies) | Global | Cross-border, international | Strong | 1-2 days |
| Real-Time Rails (RTP) | Instant | Low-Med | Domestic, expanding | Billing, peer-to-peer | Strong | Seconds |
| Paper Checks | Very slow | Low-Mod. | Domestic, Limited | Occasionally, Legacy | Medium | Days |
Why Payment Rails Matter
The following are just a few of the advantages that a business can gain from using a payment rail.
- Improved cash flow: Fast payments can give you cash on hand straight away, which is particularly true for transactions through a real-time network such as RTP. This speed significantly enhances cash flow and the overall financial management process.
- Flexible payment methods: In 2021, the value of cash transactions in the United States was only 19% of the total. Payment rails make it possible for companies to use multiple payment methods, such as cards, checks, or even some cryptocurrencies.
- Recurring payments: Service companies can definitely utilize payment rails in order to set up recurring payments. This method is especially suitable for subscriptions as well as for continuous projects.
- International expansion: Payment rails facilitate cross-border business transactions, allowing you to do business with foreign suppliers, open new markets, and make your supply chain more efficient.
What’s the right payment rail for your business?
Possibly, the most suitable payment rail for your business might not be just one. In that case, you would have to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative. For instance:
- Most of today’s consumers prefer to pay by credit or debit cards.
- ACH transfers are quick and dependable, but new fintech solutions sometimes overshadow them.
- Wire transfers are reliable; however, they are expensive.
- The SWIFT network is the mainstay of international trade.
- Paper checks are still trustworthy and inexpensive.
In the end, the decision of the most suitable option for your business will be yours to make. It is important that you try to find the right balance among the factors of speed, cost, and the increasingly concerning issues of fraud and data security.
FAQs on Payment Rail
Reliable payment rails underpin modern business. Here are answers to common questions:
Are international payment rails different from domestic ones?
Yes — international rails like SWIFT or wire are designed for cross-border payments, while domestic rails such as ACH and RTP are better suited for local transactions.
How do payment rails affect transaction fees?
Each rail charges unique fees, with ACH being the lowest and wire/SWIFT being the highest; international payments generally cost more.
Can I track a payment sent via a rail?
Most rails offer tracking with reference IDs. Wire and SWIFT transfers provide extensive tracking; ACH is limited.
What happens if a payment rail fails?
If a rail fails, the transaction is delayed or reversed. Multi-rail strategies allow fallback to ensure continued payments.
How do businesses optimize payment rail usage?
They match rails to use cases, automate selection, and use multi-rail strategies for speed, cost, and redundancy.
Can fraud occur on payment rails?
Fraud is possible, but rails deploys robust protections (encryption, KYC, compliance) to minimize risk.
Make Domestic Business Payments Smoother with Cheqly
Small businesses can use Cheqly to send domestic ACH transactions in the US free of cost, which are part of their routine financial operations, making daily financial tasks easier. This feature allows companies to maintain better control over cash flow, ensuring timely payroll and efficient vendor payments. By streamlining these essential transactions, it is not only a time saver and cost reducer but also a secure and trustworthy payment service, enabling small business owners to focus on growth and operational success.
Open your Cheqly business account now for smooth, quick domestic transfers.
