In this digitally evolving world, we can observe a shift toward the globalization of payments and different forms of business and work-related interactions. For that reason, efficiency, security, and precision are critical factors in B2B payments. Closely related to these secure financial operations, one of the most effective but unnoticed factors is the Bank Identification Number (BIN). Found in the first six to eight characters of your payment card, the BIN, or Issuer Identification Number, serves as a great tool for identifying the financial institution that issued the card, as well as for card validation and the prevention of credit card fraud.
Let’s read the article, which will cover the concept of BIN, its functions, and its importance, along with some security measures related to detecting threats such as BIN scamming.
Key Takeaways
- A Bank Identification Number (BIN) is the first six to eight digits of a payment card, which distinguishes the card’s issuer as well as its industry.
- BINs help detect fraud by tracing transactions and verifying the card’s origin, type, and issuer.
- Merchants use BINs to process and authorize payments quickly and to meet compliance standards.
- BINs support fraud prevention by validating cardholder details and identifying mismatches.
- BIN scamming is a real threat—cardholders must stay alert and protect their card information.
What is a Bank Identification Number?
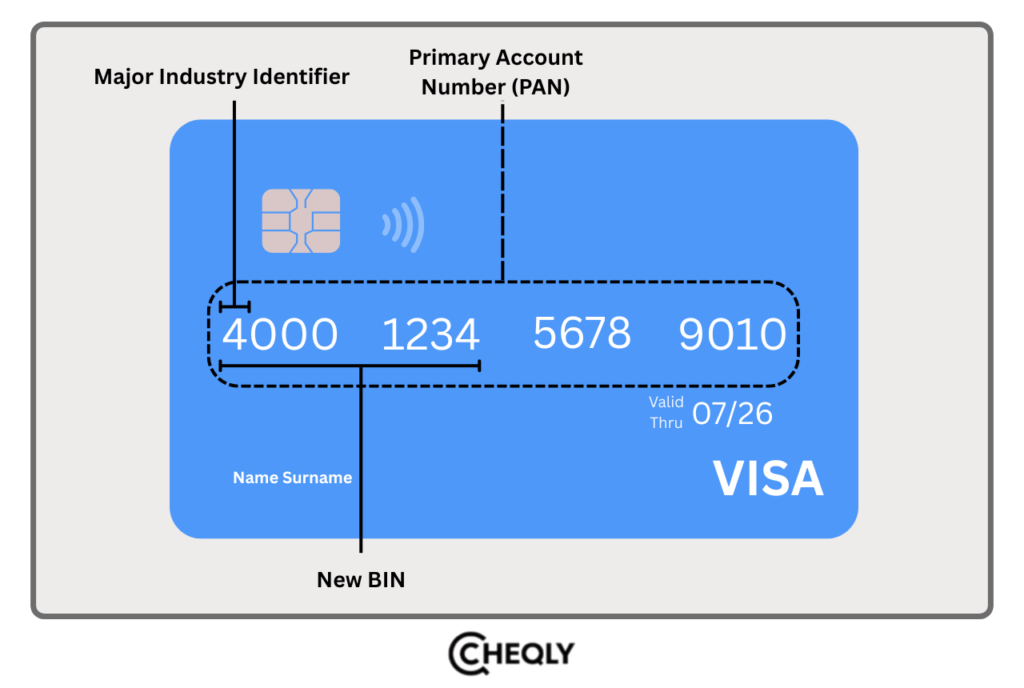
The initial six to eight digits of a payment card are known as a Bank Identification Number (BIN). Traditionally, the BIN has always consisted of six digits. However, due to recent changes, the BIN can now be eight digits long to accommodate more issuers. The initial digit of this series serves as the primary industry identifier, while the other digits represent the financial institution that issued the card. For instance, all Visa cards start with the number ‘4’, which is their Major Industry Identifier. These are embedded in credit cards, debit cards, charge cards, prepaid cards, and gift cards in order to identify the card issuer and help process transactions efficiently.
In addition, BINs are occasionally referred to as Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs) due to the fact that institutions other than banks can issue cards.
Are the Bank Identification Number and account number the same?
An account number is distinct from a bank identification number (BIN). The initial 6-8 digits of a payment card are referred to as a BIN. This identifies the type of card and the bank that has issued the current card. A BIN makes it easy to detect a lie and helps with the payment process of the bank card since it traces the origin of the card. On the other hand, the account number is a unique number that is used to recognize a given person’s account. We use it to identify and manage specific accounts for transactions like deposits, withdrawals, and transfers. The account number identifies the specific account within the institution, whereas the BIN identifies the issuing institution.
Why Do Bank Identification Numbers Matter?
BINs are quite helpful in cases of fraud, such as identity theft or the use of stolen cards, besides offering details such as the location of the card issuer, the bank that issued the card, or the type of card being used. This information can be used in conjunction with cardholder data to improve the means for flagging fraudulent charges.
Furthermore, BINs in B2B payments provide merchants with the ability to analyze and review their payment card transactions, facilitating the acceptance of various payment methods and expediting the processing of transactions.
How Do BINs Work?
The BIN system serves as a global identification tool, facilitating the identification of the issuer to which authorization requests are directed when a card is swiped or entered manually. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) were responsible for its creation. The ANSI is a nonprofit organization responsible for establishing business standards in the United States, whereas the ISO is an international nongovernmental organization that develops standards across various industries.
Every type of payment card contains a BIN number. The number is prominently displayed on the front of the card. The initial digit in the BIN sequence represents the primary industry identifier, while the subsequent digits indicate the issuing institution.
Individuals purchasing items online will input their card details on the checkout page. Upon inputting the initial six to eight digits of the card, the merchant can ascertain the institution that issued the customer’s card, along with details such as the card brand, card level (e.g., gold or platinum), card type, and the country of the issuing bank.
Every time a customer decides to make a purchase, the issuer receives an authorization request to verify the card and the account to ensure it is valid and that the purchase amount is available. This leads to the transaction being approved or rejected. BINs can be described as being fundamental to the system for processing credit cards. They help us find out the source of the customer’s funds and complete the transaction accurately.
How are BINs Utilized?
BINs serve various functions, with their primary role being to assist merchants in accurately analyzing card transactions.
Furthermore, BINs assist merchants in identifying the banks of origin and in verifying whether the banks that issued the cards are located in the same country as the device conducting the transaction. BINs also verify the address provided by the customer. That is why BINs are essential in the fight against fraud; they help identify and avoid BIN fraud. Hence, BINs help detect identity theft and other security issues by matching card details with the issuing institution.
Consumers themselves do not directly interact with BINs in most cases, thus making it important for them to be informed about the importance of BINs, as the authorization process of transactions cannot go without them. Every time a customer makes a purchase of a good or service, the institution offering the good or the service is presented with an authorization request. This request serves as a verification of the account’s legitimacy and ensures that the amount of money in the account is sufficient for the payment.
What are some advantages of BINs?
Below are some of the advantages of BIN:
- Enhancing the speed and efficiency of credit and debit card transactions.
- Upon a customer’s entry of their card information during the checkout process, the retailer’s payment processor promptly scans the cardholder’s BIN and verifies the account with the card issuer.
- Authorizing transactions and ensuring compliance.
What Is BIN Scamming?
BIN scamming is one of the techniques by which scammers get hold of credit card details. Usually, it involves a person initiating a fraudulent process by pretending to be from a certain bank. The fraudster will then proceed to call cardholders and tell them that their accounts have been hacked. They will then request the cardholder’s information to gain their trust. Afterwards, the fraudster will give the cardholder the first six or eight digits of the card and ask for the rest, thus enabling the fraudster to steal the cardholder’s credit card information as well as any other details required for unauthorized access to the funds.
Cardholders should stay alert to BIN scams and other forms of credit card fraud to protect themselves. It is important not to share card information with others and to keep financial details private.
FAQs on Bank Identification Number
The following are common answers to frequently asked questions related to BIN:
How does a BIN differ from a full card number?
A full card number, or PAN, can have up to 19 digits. The BIN usually consists of the first 6 digits, but it can be 8 digits on some cards. These digits identify the issuer, not the individual account.
What is the BIN expansion to 8 digits?
The extension of the BIN to 8 digits represents a change aimed at increasing the number of individual issuer codes required to meet the growing global demand for card issuers and payment products.
Will existing cards be reissued due to BIN expansion?
No, already issued cards remain valid; the expansion affects only new cards being issued.
Do all card networks use BINs?
Yes, BINs are used by major networks such as Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover for identification purposes.
Can two cards have the same BIN?
Yes, cards issued by the same financial institution and network can share the same BIN, especially when the issuer offers multiple card products.
How do BINs differ from ABA routing numbers?
BINs are numbers that identify the card-issuing institutions of payment cards, while ABA routing numbers are used for bank account transactions in the U.S.
How do BINs assist in compliance and security?
They help ensure compliance with regulations such as PCI DSS by making proper data handling and fraud prevention easier.
Choose Cheqly for Your Business Account!
With Cheqly, the entire process of opening a corporate account can be done quickly, and you can access financial services whenever you need them without paying any monthly fees or maintaining minimum balances. You will also be able to send money both locally and internationally with ease.
Start Your Journey with Cheqly – Open your business account today.
