Are you also eagerly looking for a correspondent bank? If yes, you are in the right place because you will find all the information here.
To handle financial activities like international wire transfers, correspondent banking usually entails domestic banks collaborating with a partner overseas bank.
Let’s begin and know everything in detail about correspondent banks.
What is a Correspondent Bank?
A correspondent bank can also be called an intermediary bank that offers services to banks transferring money internationally. Correspondent banks act as intermediaries to facilitate payments between foreign and domestic banks. They frequently facilitate foreign wire transfers, international investments, and currency exchanges.
Correspondent banks are crucial in tying together disparate banking systems since banks are unable to open branches everywhere. For example, a neighborhood bank in Duluth, Minnesota, might not have a partner in Tokyo, Japan. However, the bank in Duluth can engage in Japanese financial markets and send money to a bank in Tokyo through a correspondent bank.
How Do Correspondent Banks Work?
Correspondent banks are considered the go-between for two financial institutions because they are third-party banks. If there is no formal link between the domestic and international banks, they cannot conduct the transaction without them.
With the necessary cash, the correspondent bank receives instructions on handling various types of transactions, including currency conversion, settlement, and fund transfers. By sending such information to the other bank, it completes the transaction.
When money needs to be sent to a foreign nation, correspondent banks are the most frequently employed. The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, or SWIFT, is used for this, as it is known that SWIFT is the largest network of correspondent banks worldwide. SWIFT members include around 11,000 financial institutions in over 200 countries and territories.
Suppose the domestic bank does not already have a formal relationship with the foreign bank with which it wants to complete a transaction. In that case, it will look through the SWIFT network for a correspondent bank with a formal relationship with both banks. Once one has been located, the money will be transferred to the designated accounts maintained at the correspondent bank to start the transaction.
Vostro vs. Nostro Accounts
The nostro and vostro accounts are how correspondent banking operates. A domestic bank will open a nostro account — meaning our account, on your records in collaboration with a correspondent bank. The foreign correspondent will refer to the identical account as vostro — meaning your account on our records.
A domestic bank will locate a suitable correspondent bank and transfer funds to that bank’s nostro account to transmit money to a bank abroad. Before sending the money to its intended location, the correspondent will deduct the service charge from the transferred amount.
Example of a Correspondent Bank
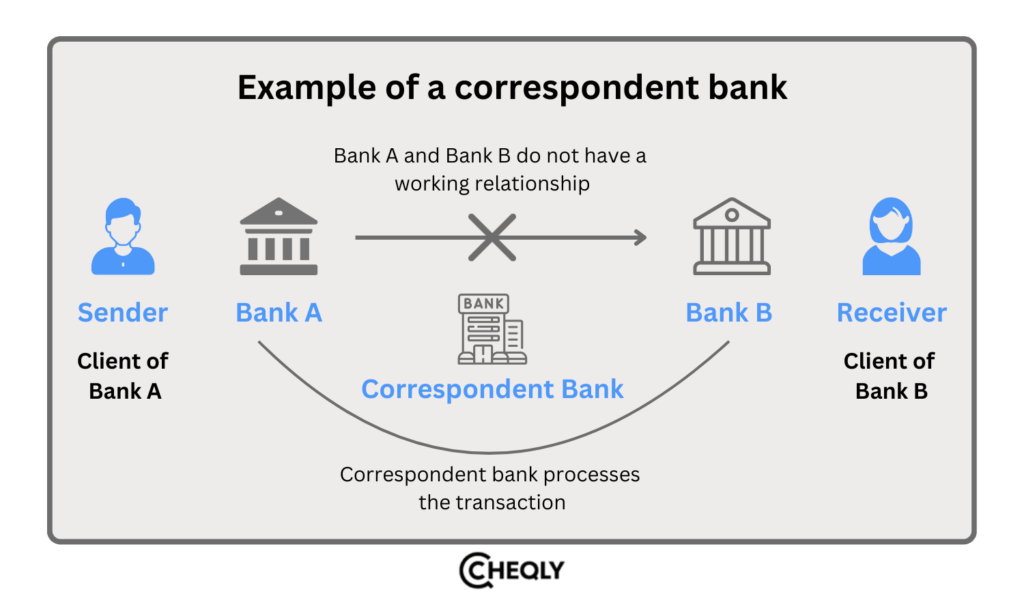
John wants to buy machinery from Singapore and must pay in Singaporean dollars to the person. The supplier must receive payment in foreign currency in an account denominated in Singaporean dollars. The transaction will have to go via the SWIFT network because the supplier’s Singaporean bank and his US bank don’t have a direct banking relationship.
Using the SWIFT network, the banker at John’s Bank will locate a correspondent bank connected to their establishment and the Singaporean bank. After locating the correspondent, John’s bank will transfer the money to the correspondent’s Nostro account, subtract a fee, and deposit the money into the receiving bank’s Vostro account.
Thus, thanks to correspondent banking, John can do business with a supplier in Singapore even though he does not have a bank account there. In the US, he doesn’t even need to switch banks.
Even if it is not affiliated with the Singaporean bank, his current bank can handle the transaction by using the SWIFT network to find a correspondent bank that can serve as an intermediary.
Difference between Correspondent Bank vs. Intermediary Bank
Both correspondent banks and intermediary banks share similarities as they both offer services to other financial institutions for a fee. Conversely, intermediary banks are more likely to provide single-currency services, even though correspondent banks typically deal in foreign exchange transactions.
You may see one or the other referring to the SWIFT payment process because the expressions are fairly interchangeable.
Key Differences Between Correspondent Banks and Intermediary Banks
| Feature | Correspondent Banks | Intermediary Banks |
| Primary Role | Facilitate banking functions for other banks | Act as a middleman between sending and receiving banks |
| Function | Handle transactions, clearances, and settlements | Route payments between banks |
| Relationship with Banks | Maintain direct accounts with other banks | Facilitate one-time or specific transactions |
| Usage | Used for ongoing financial transactions, often international | Used for international transfers when direct bank links are missing |
| International Transactions | Key for handling international transfers and services | Mainly used when there’s no direct connection between the sending and receiving banks |
| Scope of Operation | Builds long-term connections with several banks | Works temporarily to route specific payments |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Correspondent Banks
Here are the key advantages and disadvantages of correspondent banks:
Advantages
- Global Financial System: The primary advantage of correspondent banks is that they enable domestic banks to gain access to the global financial system without having branches in foreign jurisdictions. Such an undertaking will undoubtedly incur significant expenses and come with regulatory risks for financial institutions.
- Performing Cross-Border Transactions: A domestic financial institution can collaborate with a correspondent bank to provide its clientele with global funds transfers, check clearing, and associated services, all without a formal relationship with the foreign bank involved. The correspondent bank manages all aspects on its behalf.
Disadvantages
- Delay Processing Time: One disadvantage for clients is that transactions conducted through correspondent banks frequently require a longer processing time than they might anticipate. A wire transfer typically requires a processing period of several days. It appears to be an excessive delay in an era where the transfer of funds is anticipated to occur within mere seconds.
- Higher Transaction Cost: Another disadvantage is the additional expense. Correspondent banks typically charge consumers service fees. In particular, if their financial institution charges a premium on associated fees, this may significantly raise transaction costs for them. However, the higher transaction cost is also due to the fact that it ensures safe and secure international transfers.
Do Correspondent Banks Impose Fees?
Correspondent banks’ fees or charges depend on several factors, such as their type of service. The fees for international wire transfers normally vary from $25 to $75 per transaction.
The institutions disclose to customers the fees associated with these transactions. Some may add a markup to the real cost, while others may charge clients what they pay the correspondent bank.
Corresponding Banks FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about correspondent banks.
Why are correspondent banks necessary?
Correspondent banks are necessary because they are intermediaries between banks in different nations that do not have any relationships. These banks allow for cross-border payments, currency exchanges, and business deals, making the process of banking between banks smoother.
What is the difference between a correspondent bank (intermediary bank) and a beneficiary bank?
A correspondent bank facilitates international financial transactions by providing support through other banks (respondent banks) that might not have a direct presence in a particular country or market. A beneficiary bank is a financial institution that receives funds on behalf of the beneficiary from a remitting bank via an intermediary bank.
How does a correspondent bank differ from a receiving bank?
A correspondent bank is a financial institution facilitating international fund transfers on behalf of other banks. The receiving bank is the financial institution that receives and processes the funds for the recipient’s account.
How does a correspondent bank help with international wire transfers?
Correspondent banks act as middlemen for the sender’s and receiver’s banks in different countries, even though they do not have a relationship. Using a correspondent bank, you can securely perform international wire transfers with currency conversions and regulatory compliance through SWIFT networks.
What are the advantages of correspondent banks?
Correspondent banks help domestic banks access international services without costly foreign branches. They aim to make the global financial system more affordable, expedite international transactions, and reduce the associated risks. These connections provide local banks with the opportunity to offer services like wire transfers, foreign currency exchange, and trade finance, which can help them grow their offerings and reach more markets.
Experience the convenience of wire transfers with Cheqly!
Correspondent banks significantly facilitate global trade. Domestic banks couldn’t offer the financial services necessary for businesses to operate internationally without them.
No bank can operate branches in every city or maintain direct relationships with every other bank. They can only access the global financial system for their clients via the correspondent banking network.
Open a Cheqly business account today to perform wire transfers for international and domestic payments at a nominal rate. It can also help small business owners make free ACH payments within the US. By creating a business account (with no monthly fee or minimum balance requirement), you can separate your personal and professional finances, and by using a business debit card, you can easily perform ongoing transactions.
Sign up for your business account today and streamline your transactions effortlessly.
