In a nutshell, every transaction is contingent upon the successful completion of the payment cycle without delays or errors. Through payment processing, businesses are able to receive funds from their clients in various ways, such as a card swipe, online checkout, or mobile tap. However, it is a system that works invisibly in the background, ensuring that the money flow is secure from the customer to the business.
Whether stores are small or large, run online or offline, a convenient payment process can go a long way in establishing a good relationship with customers, maintaining a regular inflow of money, and reducing the number of minor issues that may arise.
This guide will explain the payment processing system, its essential components, and the best ways to make the system work effectively.
What is payment processing?
The series of steps that safely move money between a payer and a payee is known as payment processing. Usually, it entails using electronic payment systems for transaction authorization, verification, and settlement.
Some of the types of transactions that payment processing systems handle include credit and debit cards, electronic funds transfers (EFTs), automated clearing house (ACH) transfers, mobile payments, digital wallets, and cryptocurrencies.
What makes payment processing a key business operation?
Transactions run more smoothly when payment processing systems are efficient. They make it easy and painless for you, as a business, to collect money from your clients. To enable credit card payments, for instance, you may utilize a payment processor, which allows instant payment verification.
As a buyer of products and services, payment processing systems are similarly beneficial, since they make it easier for your accounts payable teams to pay supplier invoices and take advantage of early payment incentives.
Key Elements of Payment Processing
In order to enable transactions between companies and their clients, payment processing is a very complex workflow that consists of numerous components that collaborate successfully and efficiently.
The several elements that need to cooperate in order to enable efficient payment processing are listed below:
- Customer: The individual or company that starts the payment process and pays for the goods or services.
- Merchant: The company or service provider that is taking that customer’s payment.
- Payment method: The payment method that the client prefers (credit card, for example).
- Point-of-sale (POS) system: The physical or digital platform on which the transaction is conducted. This could be done using a physical point-of-sale terminal at a retail establishment or a digital mobile app.
- Payment gateway: A service provider that encrypts and secures data when transferring payment information from the point-of-sale system to the acquiring bank or payment process.
- Payment processor: A third-party organization that is responsible for the technical aspects of the payment. This includes confirming the payment, getting the required approval to withdraw money, and helping the consumer and merchant banks communicate.
- Acquiring bank, or acquirer: The merchant’s bank or other financial organization that gets the money is known as the acquirer or acquiring bank.
- Card network: Card firms that create standards and regulations and put up infrastructure for transaction processing, such as Visa or Mastercard.
- Issuing bank, or issuer: The bank or financial organization of the client that authorizes or completes the transaction.
- Payment security: Some standards and technology, including the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), assist in safeguarding transaction data, guarding against fraud, and stopping data breaches.
How does payment processing work?
There are numerous processes and stakeholders involved in the process. The following explains how payment processing operates:
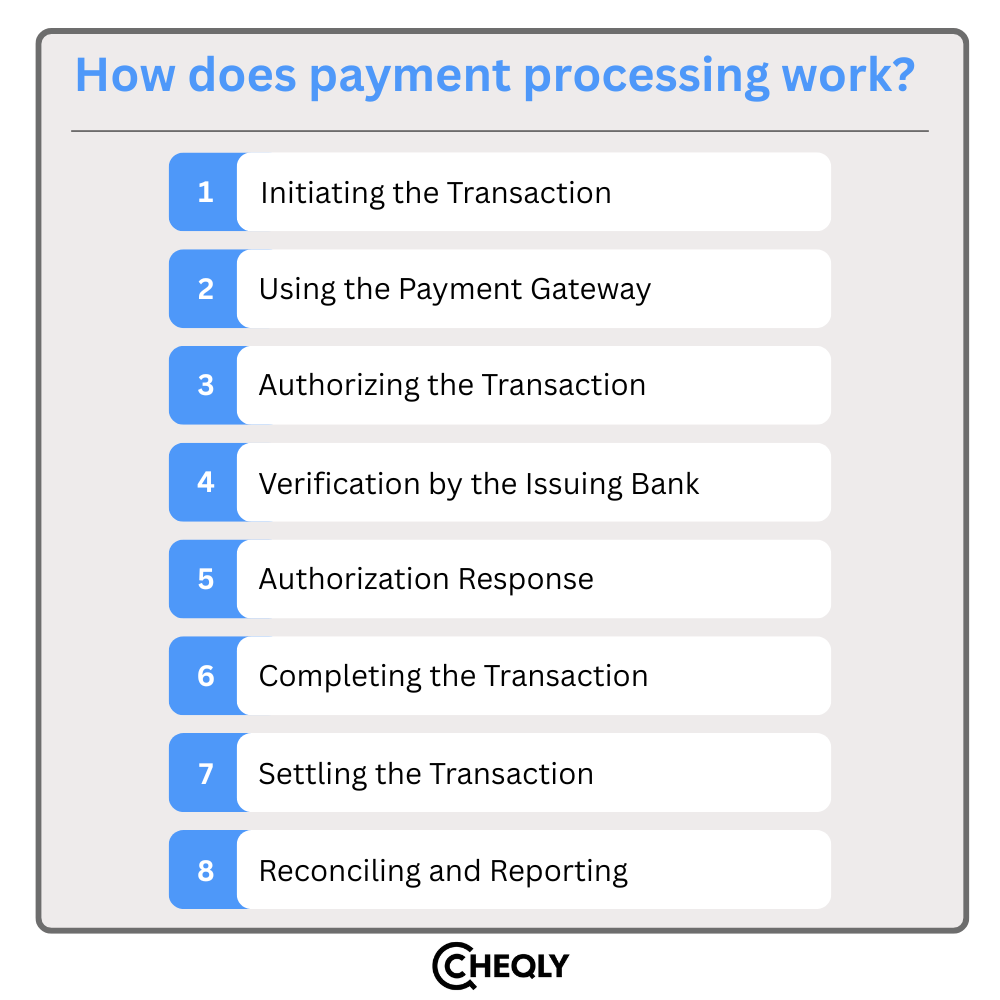
Initiating the Transaction
Payment details, such as a credit card, debit card, or another payment method provided by the customer, are required to start the payment at the point of sale in a physical store or through an e-commerce site or mobile app.
Using the Payment Gateway
Securely, the payment data is transmitted to the payment gateway, where the information is encrypted and sent further to a payment processor, the acquiring bank, and the card network for authorization and settlement.
Authorizing the Transaction
The payment processor confirms the transaction details and shares them with the acquiring bank. The acquiring bank then sends the data to the card network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard) that moves the information to the issuing bank (customer’s bank).
Verification by the Issuing Bank
The transaction data is sent through the card network to the issuing bank. The bank in question checks the available money or credit line, verifies the account status of the client, and also evaluates the situation for any potential risks. The decision whether the transaction will be authorized or not will be made by the issuing bank after such assessments have been done.
Authorization Response
The issuing bank sends the authorization response back through the card network to the payment processor, which relays it to the payment gateway. The gateway then conveys the result to the merchant’s point-of-sale system or online platform.
Completing the Transaction
The merchant will provide the goods or services if the payment is authorized. If the transaction is rejected, the merchant might ask the customer to use another payment method.
Settling the Transaction
Every day, the merchant sends the approved transactions to the payment processor or acquiring bank for settlement. After this, the acquirer requests the funds from the issuing bank through the card network’s clearing system. Once the transaction is cleared, the money is transferred from the issuing bank to the acquiring bank, and the merchant’s account is usually credited within 1 to 2 business days; however, the timing may vary depending on the region and the acquirer.
Reconciling and Reporting
The company compares the completed transactions to its sales data and any fees imposed by the acquiring bank, payment processor, or other parties.
Best Practices for Business Payment Processing
If a company follows the best practices in payment processing, the result will be increased customer satisfaction, lower fraud risk, compliance with rules and regulations, and more efficient internal procedures with fewer errors.
The following are important recommended practices for firms while processing payments:
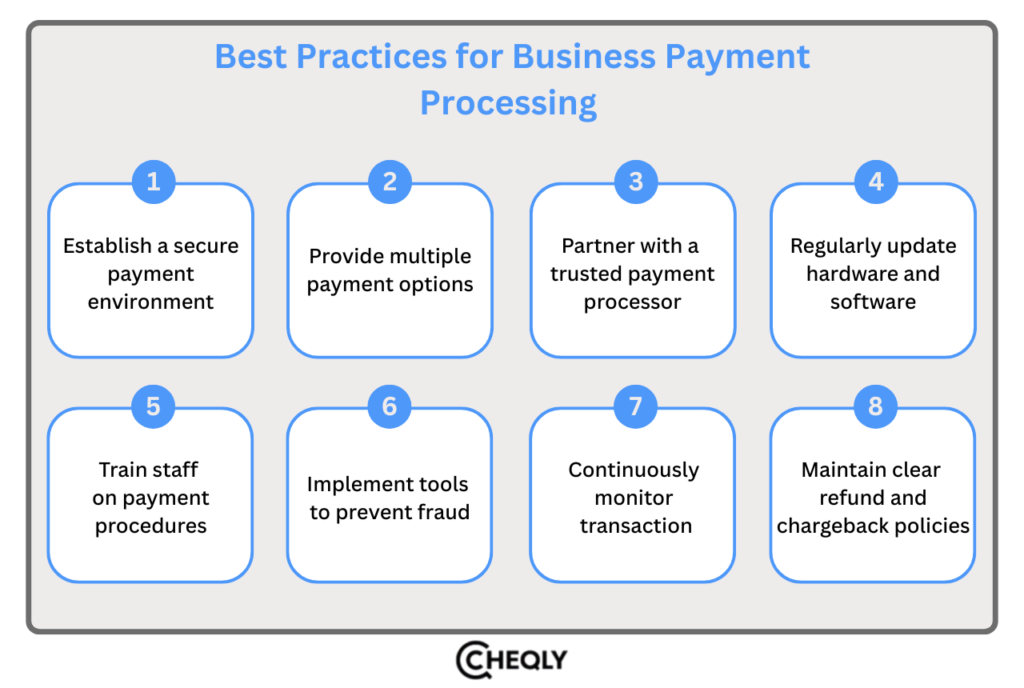
- Establish a secure payment environment: Implement strong security steps, including encryption, tokenization, and SSL, which protect payment information and create a safe payment environment by following PCI DSS and other similar standards.
- Provide multiple payment options: When customers are permitted to utilize digital wallets, credit/debit cards, and other payment methods, it is much easier for them to get the products/services they want, and it increases their level of satisfaction.
- Partner with a trusted payment processor: Go for a trustworthy and skilled payment processor that is able to give you an entire payment processing solution, high-quality anti-fraud features, affordable rates, and good customer service.
- Regularly update hardware and software: Regularly updating the security patches and technology for your payment processing software, hardware, and integrations can help minimize areas that are vulnerable to hackers and keep the system operating in an efficient and secure way.
- Train staff on payment procedures: Have your employees undergo training in the areas of security, fraud prevention, and payment processing so they can become acquainted with the potential problems that they can identify and manage in line with your company’s policies.
- Implement tools to prevent fraud: Try to avoid fraudulent activities using fraud-prevention tools like AVS, CVV verification, and 3D Secure to help reduce the occurrence of illegal transactions and the number of chargebacks.
- Continuously monitor transactions: Regularly monitoring your payment processing activities can help you spot abnormal patterns or indications of fraud. If you want warnings of any potential threats delivered instantly to you, then you should set up notification alerts.
- Maintain clear refund and chargeback policies: Come up with clear refund and chargeback policies and communicate them to your customers in order to reduce disputes and misinterpretations. Provide sufficient customer support to decrease the possibility of chargebacks and to resolve issues quickly.
FAQs on Payment Processing
The following are some common frequently asked questions on payment processing:
How can businesses secure their payment processing system?
Utilize strong encryption and tokenization, rely on trustworthy payment gateways, and embrace compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to protect sensitive information from being accessed by criminals.
What is transaction settlement?
A settlement is the final stage in a transaction where the payment is confirmed and the funds move from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s account.
How can businesses prevent fraud in payment processing?
It is necessary to employ software specialized in detecting fraud, oversee transactions as they happen, verify the identity of customers, and train employees so that they are able to recognize illicit activities.
Why is reconciliation important in payment processing?
Reconciliation verifies that all money coming into the business is what has been recorded in the sales and helps to reduce errors as well as improve accounting accuracy.
How often should businesses reconcile transactions?
It would be ideal to perform the reconciliation daily, or at each settlement batch, so that any discrepancies can be detected promptly.
How does PCI compliance affect payment processing?
PCI compliance provides a standardized way of ensuring the security of credit card details, whether in the storage, handling, or transmission of the data, thereby maintaining the trust of the industry by keeping the data safe from any potential breaches.
Wire Transfers Made Easy for Small Businesses with Cheqly
Cheqly enables small businesses to make wire transfers easily and effectively by simplifying both domestic and international payments. The whole process is effortless, quick, secure, and transparent, with no surprises in the fees and real-time tracking that gives you the exact location of your money. In this manner, Cheqly becomes more efficient in saving entrepreneurs time, allowing them to allocate more of it to business growth rather than payment management.
Create your Cheqly business account now for easy and efficient wire transfers.
